Introduction
In the evolving landscape of API development, selecting the right framework and approach is crucial to addressing your project’s specific needs. This solution demonstrates the creation of Employee CRUD APIs using seven distinct approaches in .NET 9.0, showcasing diverse technologies and methodologies. To ensure reliability and performance, K6 scripts have been meticulously crafted for each API type, automating validation and performance testing.
This article provides an in-depth overview of the project setup, highlights the unique strengths of each API style, and introduces the robust validation framework implemented with K6.
For a hands-on experience, explore the complete solution on GitHub:
https://github.com/venuthomas/API_7_Ways
Project Structure Overview
The solution, vT.ApiModes.sln, showcases seven different API frameworks and methodologies:
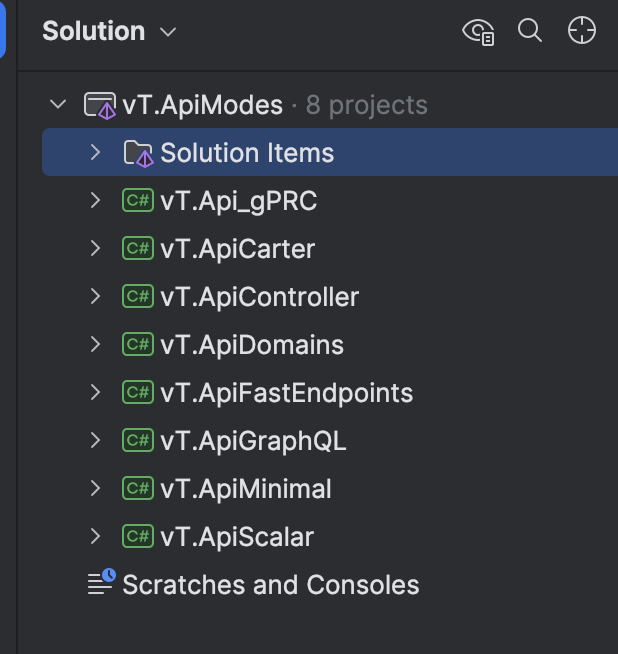
- gRPC (
vT.Api_gPRC.csproj) – High performance remote procedure calls. - Carter (
vT.ApiCarter.csproj) – A lightweight and flexible API framework. - Controller-based (
vT.ApiController.csproj) – A traditional MVC approach. - FastEndpoints (
vT.ApiFastEndpoints.csproj) – A streamlined way to define endpoints. - GraphQL (
vT.ApiGraphQL.csproj) – Advanced querying capabilities for precise and efficient data fetching.. - Minimal API (
vT.ApiMinimal.csproj) – Simplicity and speed in setting up endpoints. - Scalar API (
vT.ApiScalar.csproj) – Offline first, OpenAPI-powered API client
Common Components
All approaches are supported by a shared domain project, vT.ApiDomains.csproj, which includes:
- Polly for fault-tolerant and resilient systems.
- Entity Framework Core for ORM.
- CQRS pattern with MediatR for command and query processing.
- FluentValidation for robust data validation.
Detailed API Approaches
1. gRPC
gRPC (gRPC Remote Procedure Calls) is a modern, high-performance framework designed for inter-service communication. It leverages HTTP/2 for transport, Protocol Buffers (protobuf) for efficient serialization, and built-in support for bi-directional streaming. https://grpc.io/
Key Features:
- Performance: Binary serialization makes gRPC faster and more compact than JSON or XML.
- Streaming: Supports client, server, and bi-directional streaming for real-time communication.
- Cross- Compatibility: Works seamlessly across multiple programming languages, making it ideal for polyglot microservices architectures.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Scenarios requiring low-latency, high-throughput communication.
- Real-time applications like chat services, live streaming, and gaming.
- Inter-service communication in distributed systems.
NuGet Package:
dotnet add package Grpc.AspNetCoreProgram.cs Configuration:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddGrpc();
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapGrpcService<YourGrpcService>();
app.Run();2. Carter
Carter is a lightweight library that simplifies building APIs by removing the boilerplate associated with traditional controller-based APIs. It enables defining endpoints in a modular way using the IModule interface. https://github.com/CarterCommunity/Carter
Key Features:
- Minimalistic Design: Focuses on simplicity and modularity, reducing code clutter.
- Middleware-Friendly: Integrates smoothly with the ASP.NET Core middleware pipeline.
- Flexibility: Allows the use of existing ASP.NET Core features like dependency injection and middleware.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Projects where rapid prototyping is a priority.
- Small-to-medium applications requiring clean, modular APIs.
- Developers looking for simplicity without sacrificing flexibility.
NuGet Packages:
dotnet add package Carter Program.cs Configuration:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddCarter();
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapCarter();
app.Run();3. Controller-based API
The controller-based approach is the most traditional method in ASP.NET Core for building APIs. It adheres to the MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern, which promotes a clear separation of concerns.
Key Features:
- Structure and Convention: Controllers provide a structured way to organize endpoints.
- Middleware Integration: Fully supports ASP.NET Core’s middleware features like authentication and authorization.
- Extensibility: Easily integrates with tools like Swagger for API documentation.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Scenarios requiring extensive use of middleware, validation, and filters..
- Large-scale applications with complex business logic.
- Teams with developers already familiar with the MVC pattern.
NuGet Packages:
dotnet add package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc
dotnet add package NSwag.AspNetCore Program.cs Configuration:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddControllers();
builder.Services.AddOpenApiDocument();
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseOpenApi();
app.UseSwaggerUi3();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();4. FastEndpoints
FastEndpoints is a minimalistic library for defining API endpoints in a concise and readable manner. It eliminates the need for controllers and leverages attributes and conventions for configuration. https://fast-endpoints.com/
Key Features:
- Speed and Simplicity: Reduces boilerplate and improves development speed.
- Customizability: Gives developers fine-grained control over endpoint behavior.
- Performance: Optimized for fast request handling with minimal overhead.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Developers looking to maximize efficiency and maintainability.
- Applications where reducing code complexity is crucial.
- Scenarios requiring fine-tuned control over the HTTP request lifecycle.
NuGet Packages:
dotnet add package FastEndpointsProgram.cs Configuration:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddFastEndpoints();
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseFastEndpoints();
app.Run();5. GraphQL
GraphQL is a query language for APIs that enables clients to request only the data they need. It’s highly flexible, allowing clients to define their own data structure. https://graphql.org/
Key Features:
- Client-Driven Queries: Clients can specify exactly what data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching.
- Schema-Based: A strongly-typed schema defines all possible queries, mutations, and subscriptions.
- Real-Time Capabilities: Supports subscriptions for live updates.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Scenarios involving dynamic or evolving data requirements.
- Applications with complex data models and relationships.
- Projects requiring a single API for multiple clients (e.g., web and mobile apps).
NuGet Packages:
dotnet add package HotChocolate.AspNetCoreProgram.cs Configuration:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services
.AddGraphQLServer()
.AddQueryType<Query>()
.AddMutationType<Mutation>();
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => endpoints.MapGraphQL());
app.Run();6. Minimal API
Minimal APIs provide a simplified approach to building lightweight APIs. Introduced in .NET 6, they allow developers to define endpoints directly in the Program.cs file, making setup quick and easy.
Key Features:
- Ease of Use: Minimal APIs reduce boilerplate and setup complexity.
- Rapid Prototyping: Ideal for quickly building small-scale APIs or microservices.
- Extensibility: Can still leverage ASP.NET Core’s middleware and dependency injection.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Developers seeking simplicity without sacrificing ASP.NET Core’s power.
- Microservices or serverless applications.
- Proof-of-concept projects or rapid prototypes.
NuGet Packages:
dotnet add package Microsoft.AspNetCore.AppProgram.cs Configuration:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapGet("/endpoint", () => "Hello World!");
app.Run();7. Scalar API
Scalar is an offline-first API client built for OpenAPI, making it a powerful tool for interactive API development. It integrates seamlessly with popular frameworks like FastAPI, Elysia, and Hono, providing a developer-friendly experience. https://scalar.com/
Key Features:
- First-class OpenAPI/Swagger support.
- Interactive API references with dynamic parameters and request examples.
- Watch Mode for real-time syncing with server frameworks.
- Built-in API playground for testing and debugging.
Ideal Use Cases:
- API testing, offline development, and documentation-first workflows.
NuGet Packages:
dotnet add package Scalar.AspNetCoreProgram.cs Configuration:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddScalar();
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseScalar();
app.Run();Domain Logic with vT.ApiDomains
The vT.ApiDomains.csproj includes extension methods for seamless integration:
AddDomainService: Configures MediatR, CQRS, validation, and Polly fault handling.MapDefaultEndpoints: Simplifies database migration and endpoint mapping.
Integration is as simple as:
builder.AddDomainService();
app.MapDefaultEndpoints();Validating APIs with K6
For each API type, K6 scripts have been meticulously crafted to automate testing of CRUD operations—Create, Read, Update, and Delete. These tests ensure consistent performance, reliability, and responsiveness, providing a robust validation layer before deployment. The scripts simulate real world scenarios and workloads, enabling teams to evaluate how their APIs handle various conditions, from high traffic to edge cases.
To get started with K6, refer to the installation guide here: https://grafana.com/docs/k6/latest/set-up/install-k6/.
The K6 scripts are organized and available under the K6Testing folder for easy access and execution.
Here’s an example script for testing the “Fetch All Employees” endpoint via the FastEndpoint API approach. This script demonstrates K6’s capabilities in validating API responses for status, performance, and structure.
Example Script: Fetch All Employees via FastEndpoint
import http from 'k6/http';
import { check, sleep } from 'k6';
export const options = {
iterations: 10, // Execute 10 requests for this endpoint
};
export default function () {
const url = 'http://localhost:12084/api/fastEndpointAPI/GetAllEmployee';
const response = http.get(url);
check(response, {
'is status 200': (r) => r.status === 200, // Ensure the response status is 200
'response time < 75ms': (r) => r.timings.duration < 75, // Verify the response time
'content type is JSON': (r) => r.headers['Content-Type'].includes('application/json'), // Confirm JSON response
'response body contains employees': (r) => JSON.parse(r.body).length > 0, // Check if the response body contains data
'has expected fields (id, firstName, lastName, age)': (r) => {
const employees = JSON.parse(r.body);
return employees.every(e =>
e.hasOwnProperty('id') &&
e.hasOwnProperty('firstName') &&
e.hasOwnProperty('lastName') &&
e.hasOwnProperty('age')
);
},
});
sleep(1); // Pause for a second between iterations
}
Key Highlights of the Script
- Iterations: The script is configured to make 10 requests (
iterations: 10) to simulate real-world API usage. - Performance Check: The response time is validated to be less than 75ms, ensuring optimal performance under load.
- Response Validation: It verifies the status code, content type, and structure of the response body.
- Field Validation: Ensures the response contains the required fields—
id,firstName,lastName, andage. - Dynamic Workflows: By incorporating real-world scenarios, this script ensures the API can handle varying workloads effectively.
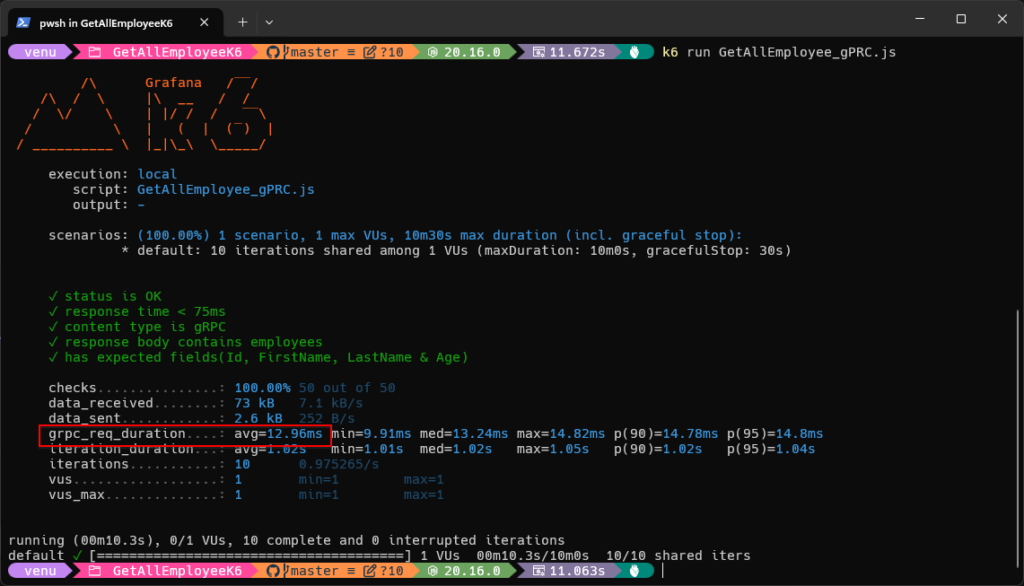
Screenshot of K6 Testing Results Using the gRPC’s K6 Script for ‘Get All Employee’ API with 10 Requests:
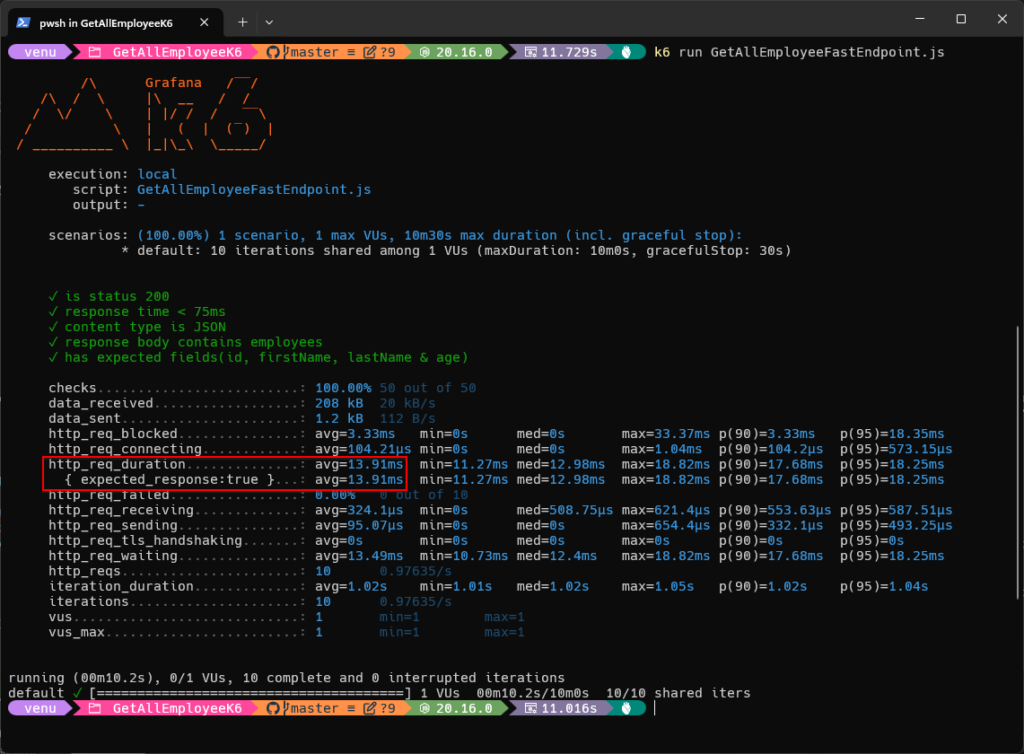
Screenshot of K6 Testing Results Using the FastEndpoint’s K6 Script for ‘Get All Employee’ API with 10 Requests:
Screenshot of K6 Testing Results Using the GraphQL’s K6 Script for ‘Get All Employee’ API with 10 Requests:
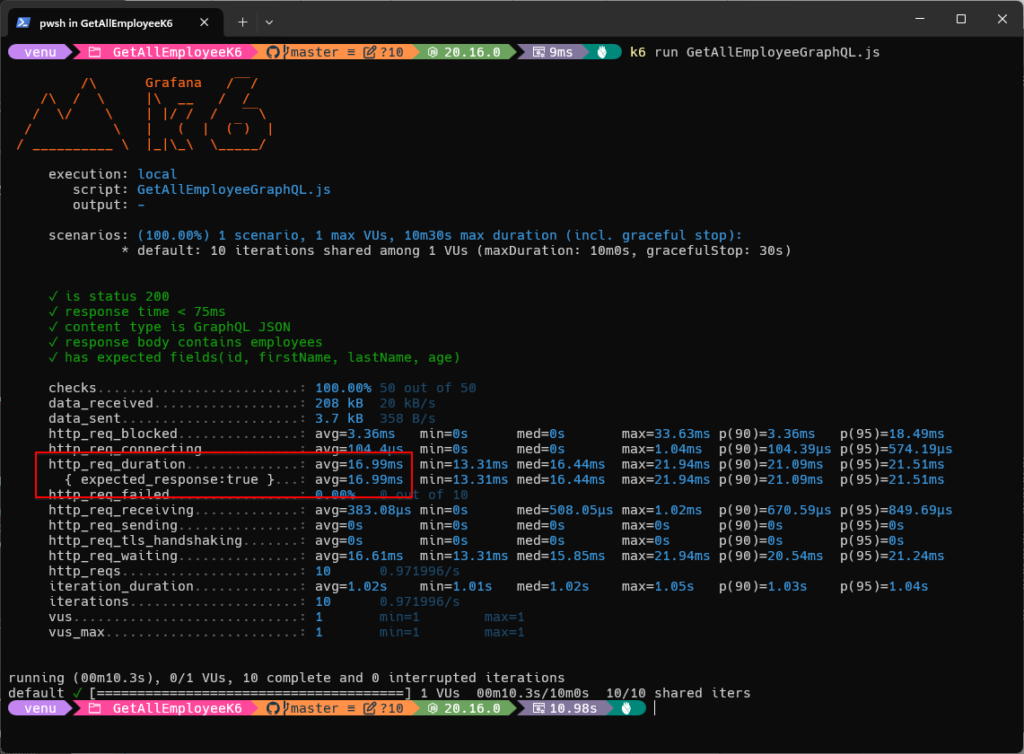
Screenshot of K6 Testing Results Using the Minimal’s K6 Script for ‘Get All Employee’ API with 10 Requests:
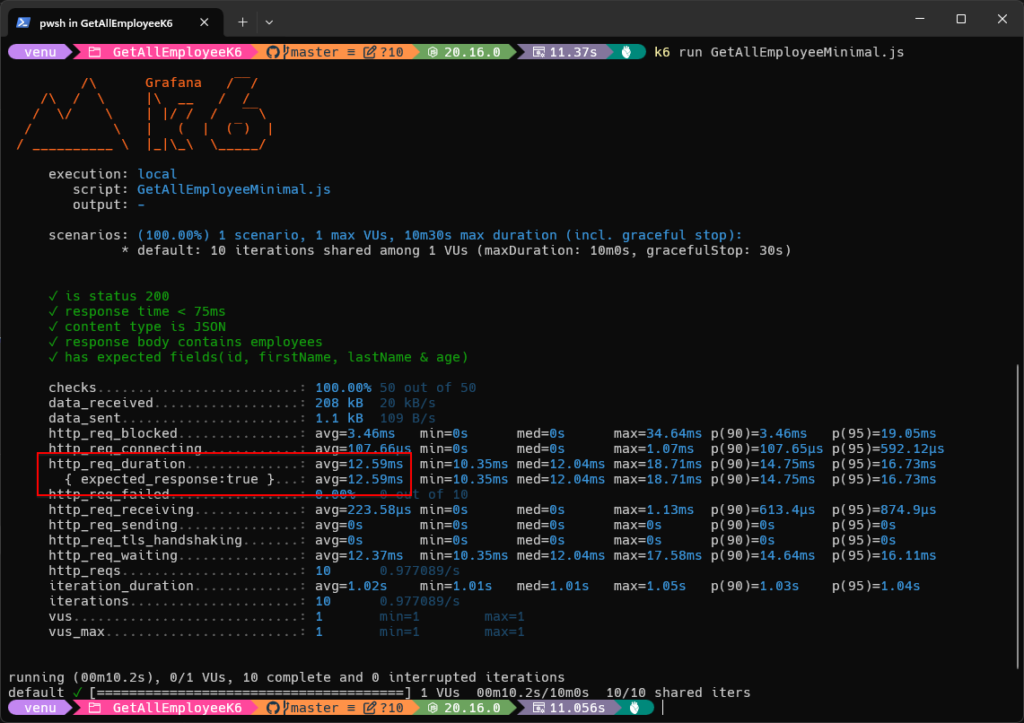
Conclusion
This project offers a comprehensive exploration of multiple API frameworks in a single solution, providing insights into the strengths and trade-offs of each approach. Whether you need high-speed communication with gRPC, dynamic querying with GraphQL, or rapid development via Minimal APIs, this solution empowers developers to choose the most suitable paradigm for their needs.
If you have any more questions or need further clarification, feel free to ask!