A simple and fun guide for developers getting started with AI in .NET
In 2024, developers were busy experimenting with AI, poking at prompts, building tiny chatbots, and pretending to be data scientists for a hot minute.
But 2025? Oh, it’s the dawn of the AI Agent Era. Programs aren’t just answering questions anymore; they are thinking, planning, and acting like your most reliable virtual teammates (minus the awkward small talk at the water cooler).
If you’re knee-deep in .NET, C#, or Azure, rejoice. Microsoft and the open-source wizards have armed you with everything needed to craft smart, self-aware apps, no Python pilgrimage required.
And with .NET 10 launching next week at .NET Conf (November 11–13), expect even juicier upgrades like built-in vector database support in EF Core and a runtime that’s 20% faster for AI workloads.
This guide breaks down the top AI frameworks for .NET in 2025, kept simple, sprinkled with ideas, and written to make sure you don’t fall asleep halfway through. Whether you’re a beginner dipping your toes or a seasoned dev eyeing AI agents, let’s build something that thinks faster than your last code review.
No PhD or crystal ball needed, just your laptop, a coffee, and 10 minutes. Here’s how to get started:
- Grab the .NET SDK: Download .NET 9 (stable) or the .NET 10 preview from dotnet.microsoft.com. The .NET 10 AI updates like GPU-friendly inference drop at .NET Conf. You can stream it live for free.
- Set up your IDE: Use Visual Studio 2022 or VS Code with the C# extension pack. Turn on GitHub Copilot for a coding buddy, but note that its older extensions retire on November 10. MCP is the new secure standard for AI tools and agents.
Alright, let’s explore the best AI frameworks every .NET developer should know in 2025.
1. Semantic Kernel
Semantic Kernel (SK) is Microsoft’s open-source brain for .NET apps. It helps your code talk to AI models like GPT, Phi, or Mistral and actually do something with the answers like reason, plan, or call APIs.
You can define skills (small AI functions) and plans (multi-step tasks) that your app can reuse. It plugs directly into Azure AI and fits perfectly inside any .NET project. Think of it as giving your C# app a mini brain that never sleeps and doesn’t need coffee breaks.
Best for: Chat assistants, smart forms, or automation inside your apps.
NuGet: https://www.nuget.org/packages/Microsoft.SemanticKernel
Docs: https://learn.microsoft.com/semantic-kernel/
GitHub: https://github.com/microsoft/semantic-kernel
Examples on my previous articles:
- How We Use AI in Our Projects: https://wisecodes.venuthomas.in/2025/04/21/how-we-use-ai-in-our-projects-a-simple-example-with-address-entry/
- Building an AI-Powered Grocery Ordering Assistant with Semantic Kernel: https://wisecodes.venuthomas.in/2025/09/09/building-an-ai-powered-grocery-ordering-assistant-with-semantic-kernel/
2. Microsoft Agent Framework
If Semantic Kernel is the brain, the Microsoft Agent Framework is the manager. It helps your app organize tasks, handle multiple agents, and keep everything running smoothly.
It builds on top of Semantic Kernel and .NET Aspire and gives you the tools to create, orchestrate, and deploy intelligent agents that can even self correct. Think of it as the manager that never forgets deadlines or needs a reminder email.
It integrates with Azure, supports evaluation tools, and makes it easy to monitor performance across your AI ecosystem.
Best for: Multi-agent workflows, business automation, or AI copilots for enterprise apps.
NuGet: https://www.nuget.org/packages/Microsoft.AgentFramework
Docs: https://learn.microsoft.com/dotnet/ai/agents/
GitHub: https://github.com/microsoft/agent-framework in .NET – The Next Step Beyond Semantic Kernel
Read about it in my previous article:
Getting Started with Microsoft Agent Framework: https://wisecodes.venuthomas.in/2025/10/13/getting-started-with-microsoft-agent-framework-in-net-the-next-step-beyond-semantic-kernel/
3. AutoGen (.NET Version)
AutoGen is Microsoft’s framework for building AI teams that talk and collaborate. Imagine having one AI that gathers data, another that checks it, and another that writes the summary. It’s like a digital office where everyone actually does their job.
It also comes with AutoGen Studio, a low-code interface that helps you visually design how agents interact. It’s easy to use, and great if you want your AIs to share work instead of arguing about who’s in charge.
Best for: Research automation, multi-agent systems, and decision-making applications.
NuGet: https://www.nuget.org/packages/Microsoft.AutoGen
Docs: https://aka.ms/autogen-studio
GitHub: https://github.com/microsoft/autogen
4. Microsoft.Extensions.AI
Microsoft.Extensions.AI is the quiet foundation under most .NET AI frameworks. It connects your app to AI models easily and efficiently without requiring a full setup.
You can use it to send prompts, stream chat responses, or work with embeddings. It’s fast, light, and dependable. Think of it like the wiring in your house, nothing fancy, but everything depends on it working correctly.
Best for: Simple AI integration inside APIs or background services.
NuGet: https://www.nuget.org/packages/Microsoft.Extensions.AI
Docs: https://learn.microsoft.com/dotnet/ai/overview
GitHub: https://github.com/dotnet/extensions/tree/main/src/Libraries/Microsoft.Extensions.AI
Read my previous article:
Your First AI Application in .NET – A Step-by-Step Guide: https://wisecodes.venuthomas.in/2025/09/21/your-first-ai-application-in-net-a-step-by-step-guide/
5. Local LLM: LLamaSharp or Foundry Local CLI
Sometimes you don’t want your AI talking to the internet. Maybe you want it private, offline, or just cheaper to run. That’s where local LLMs (Large Language Models) come in. They let you run AI directly on your own computer.
a. LLamaSharp
LLamaSharp is a .NET wrapper for llama.cpp. It lets you run models like LLaMA 3 or Mistral locally.
You control everything, hardware, model size, and memory. It’s great for when you want to cook your own AI instead of ordering takeout.
Best for: Offline or private apps that need full control.
NuGet: https://www.nuget.org/packages/LLamaSharp
Docs: https://scisharp.github.io/LLamaSharp/0.4/?utm_source=chatgpt.com
GitHub: https://github.com/SciSharp/LLamaSharp
Read my previous article about Basics:
AI Model Basics – Understanding Size, Hardware and Setup: https://wisecodes.venuthomas.in/2025/08/24/ai-model-basics-understanding-size-hardware-and-setup/
b. Foundry Local CLI
Foundry Local CLI is Microsoft’s easier option for running models locally. It handles optimization for your hardware automatically, so you can focus on building your app. It’s part of Azure AI Foundry and can later move to the cloud with almost no code change.
It’s perfect for developers who want to test models fast and locally without spending time on setup.
Best for: Quick local AI setup and hybrid local-cloud projects.
NuGet: https://www.nuget.org/packages/Microsoft.AI.Foundry.Local
Docs: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-foundry/foundry-local/get-started
GitHub: https://github.com/microsoft/Foundry-Local
6. LM-Kit.NET
Multimodal magic: Text, images, and voice in one SDK. LM-Kit.NET lets your .NET apps understand and respond using multiple senses at once. Perfect for IoT or edge devices that need awareness beyond sight.
If Semantic Kernel gives your app brains, this SDK adds eyes, ears, and the ability to throw in a witty comeback. It’s built for offline or hybrid scenarios where speed and privacy matter most.
Best for: Voice and image apps, smart edge AI systems, and embedded devices that need a bit of
NuGet: https://www.nuget.org/packages/LM-Kit.NET
Docs: https://lm-kit.com/solutions/ai-agents
GitHub: https://www.nuget.org/packages/LM-Kit.NET
7. BotSharp
BotSharp is an open-source framework for building chatbots with memory and reasoning in C#. It’s perfect for creating bots that can have a real conversation and remember context.
If you’ve ever yelled “that’s not what I meant” at a chatbot, BotSharp will help fix that. It’s easy to customize and extend for business use.
Best for: Customer support bots or internal company assistants.
NuGet: https://www.nuget.org/packages/BotSharp.Core
GitHub: https://github.com/SciSharp/BotSharp
8. Agent2Agent SDK
Agent2Agent (A2A) is like a friendly walkie-talkie for your AI helpers. It lets different AI “friends” (called agents) talk to each other, share what they know, and work as a team , without getting lost or shouting across the playground.
Think of it like this:
- Research Kid looks up fun facts.
- Summary Pal turns those facts into short notes.
- Storyteller uses those notes to write a story.
Without A2A, each one works alone, forgetting to share the ball. With A2A, they pass notes, share ideas, and finish the task together. like good teammates on the same project.
Created by Microsoft in July 2025, it’s designed to help your AI agents cooperate smoothly instead of acting like lonely robots. You could say it’s teamwork for machines, minus the noise of Slack messages or random “quick call?” requests.
Best for: Making separate AI agents work together on tasks like research, summaries, reports, or creative storytelling.
NuGet: https://www.nuget.org/packages/A2A/0.3.3-preview
Docs: https://devblogs.microsoft.com/foundry/building-ai-agents-a2a-dotnet-sdk/
GitHub: https://github.com/a2aproject/a2a-dotnet
9. Model Context Protocol (MCP)
MCP defines how AI agents connect to real-world data and tools safely. It’s what allows them to use APIs, access databases, or open browsers.
It’s like a universal translator that makes sure your AI stays smart but doesn’t accidentally delete the database. MCP is also the backbone of GitHub Copilot’s new secure tool system.
Best for: Agents that need to integrate with external systems.
Docs: https://microsoft.github.io/mcp/
Read my previous article:
AI Replacing the Browser – Exploring Model Context Protocol (MCP): https://wisecodes.venuthomas.in/2025/07/22/ai-replacing-the-browser-exploring-model-context-protocol-mcp/
The Simple .NET AI Stack for 2025
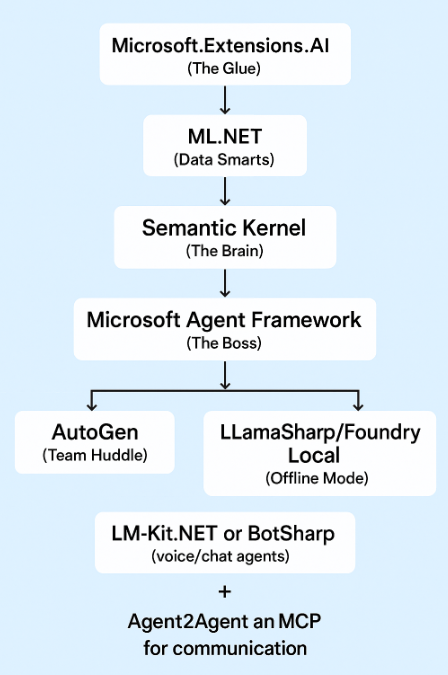
Summary: From Experiment to Essential
AI in .NET isn’t sci-fi anymore. it’s your next pull request. You can now build assistants, automations, or full-blown agent networks right inside your familiar C# world.
Start Small (Beginner Roadmap):
- Learn ML.NET for data and prediction basics.
- Dive into Semantic Kernel. it’s your AI brain.
- Orchestrate smart workflows with Microsoft Agent Framework.
- Make your agents collaborate using AutoGen.
- Go local with LLamaSharp or Foundry Local for offline brains.
- Power up with MCP and Agent2Agent for advanced coordination.
- Upgrade to .NET 10 after .NET Conf for faster runtime and built-in vector support.
If your app starts giving you code review feedback, don’t panic, that just means it’s working
Quick Decoder Ring
Agent: An AI that can plan and act. basically your tireless virtual intern.
LLM: Short for Large Language Model the world’s most overqualified autocomplete.
Orchestration: The art of making multiple AIs work together without chaos (herding smart cats).
RAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation . mixing AI with real data so it stops making stuff up.
MCP: Model Context Protocol, the standard way AIs safely talk to tools, browsers, and APIs.
Vector Database: A special kind of database for storing and searching AI knowledge fast.
Multimodal: Fancy word for AIs that handle text, voice, and images all at once.
Building AI in .NET today feels like giving your old app a brain upgrade. It’s smarter, faster, and yes, probably judging your variable names, but in a helpful way.
Happy Coding!